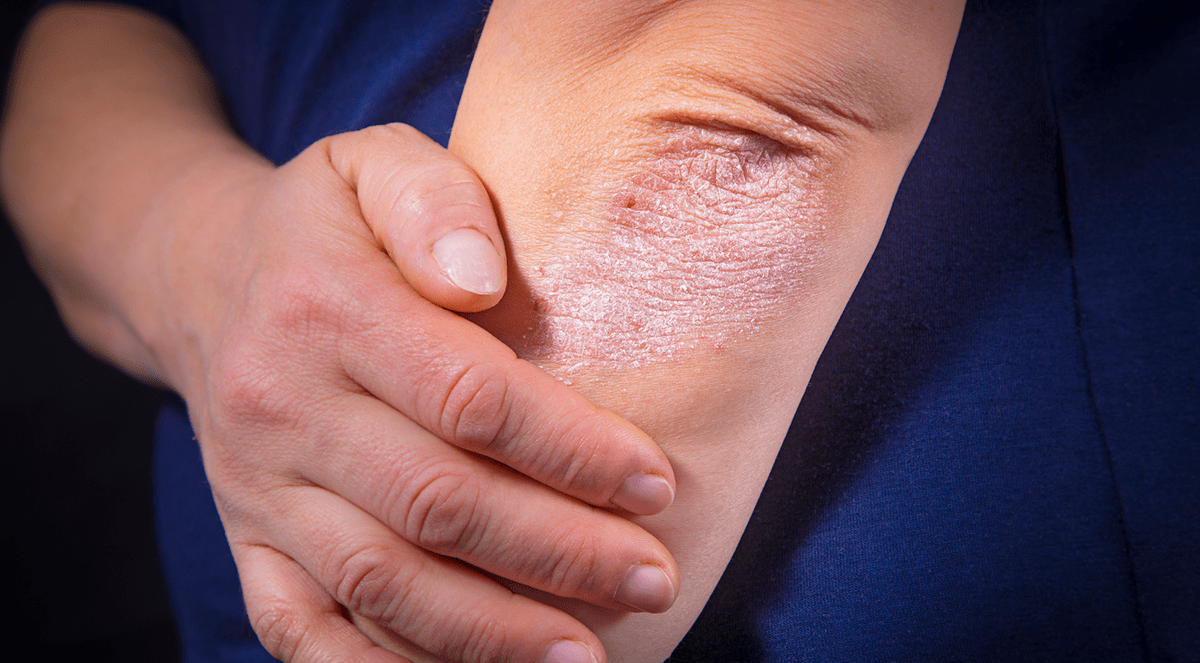
Patients with psoriasis frequently experience fatigue. Though conventional medications have little impact on tiredness in general, biological agents have shown to be useful in a variety of other chronic inflammatory disorders. The study sought to assess the effect of biological medicines on tiredness in patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris.
Researchers performed a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials in which anti-interleukin-12/23, anti-interleukin-23, anti-interleukin-17, or anti-tumor necrosis factor- agents were used to treat psoriasis Vulgaris and tiredness was employed as an end measure.
The meta-analysis included 8 randomized controlled studies that met the inclusion criteria. The fatigue reporting measures utilized in the trials were the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue and the Short Form 36 Health Survey Vitality Subscale. Treatment with biological agents, in general, resulted in a considerable reduction in fatigue, with a standardized mean difference of 0.40 when compared to placebo.
Biological medicines used to treat psoriasis Vulgaris show a constant small-to-moderate positive impact on tiredness, regardless of medication type.
Reference: link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40257-019-00434-w