The following is a summary of “Safety and efficacy of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors in relapsed and refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 20 prospective studies,” published in the March 2023 issue of Hematology by Sun, et al.
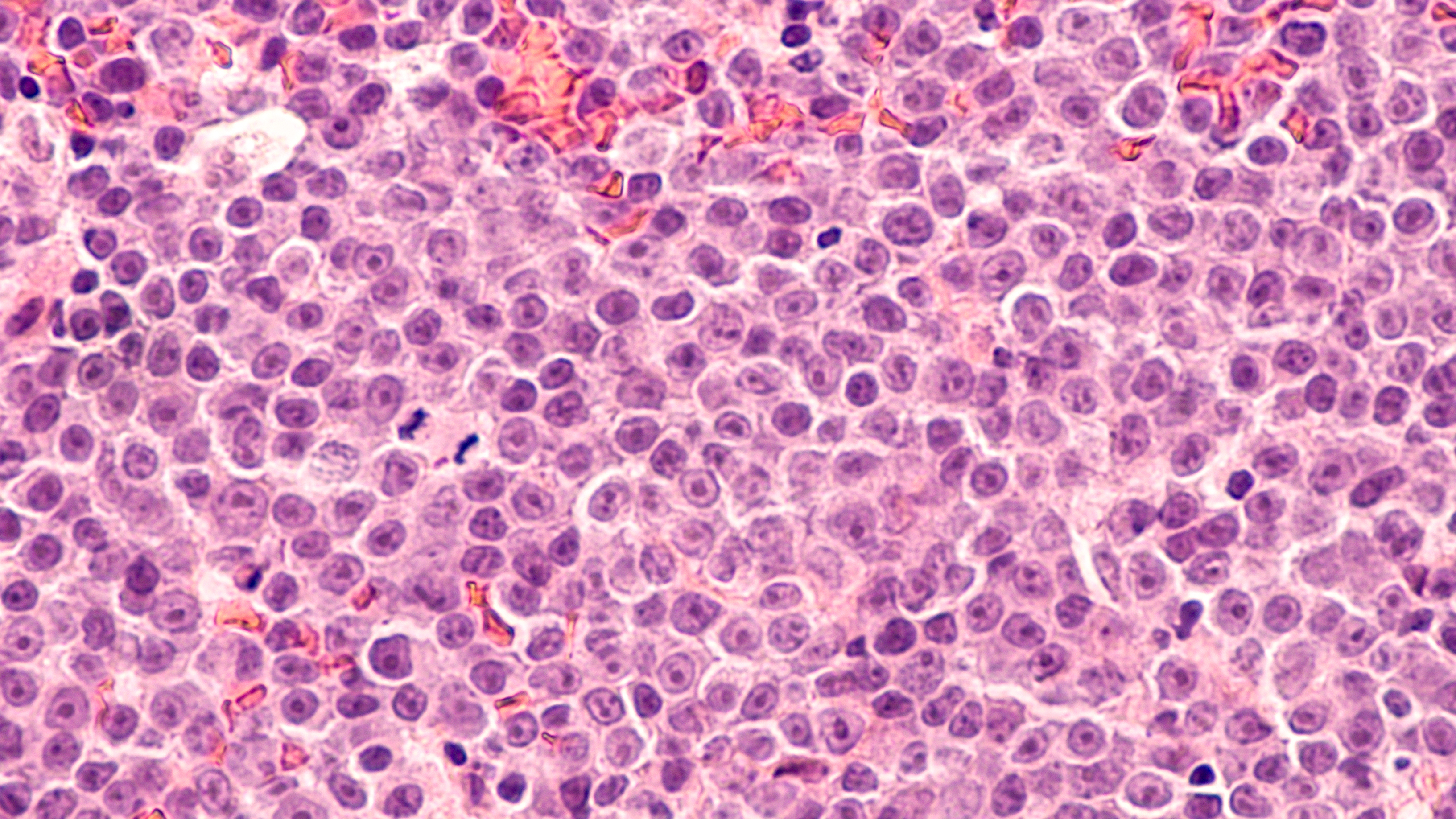
In recent years, relapsed and refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma (R/R HL) has been treated using drugs that inhibit the programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) proteins involved in programmed cell death. For a study, researchers evaluated the safety and efficacy of inhibitors of PD-1 and PD-L1 in patients with R/R HL.
A systematic search of databases and Clinical Registration Platforms was conducted for related studies up to March 2022. The incidence and exhibition of adverse effects (AEs) were evaluated for safety analysis. At the same time, overall response rate (ORR), complete response (CR) rate, partial response (PR) rate, progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and duration of response (DOR) were calculated for efficacy analysis. The package Meta and MetaSurv of software R 4.1.2 was used for analysis.
A total of 20 studies and 1,440 patients were included. Grade 3 or higher AEs had a 26% and 92% pooled incidence, respectively. The ORR, CR, and PR rates were 79%, 44%, and 34%. The most frequent adverse reactions (AEs) were leukopenia (25%), neuropathy (29%), nausea (27%), and pyrexia (26%). Leukopenia (10%), infusion reaction (8%), weight increase (3%), and neutropenia (2.7%) were the AEs with grade 3 or higher that were most frequently reported. Compared to nivolumab monotherapy, pembrolizumab monotherapy looked to perform better.
Inhibitors of PD-1/PD-L1 showed promising efficacy and tolerable AEs in the treatment of R/R HL.
Source: tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/16078454.2023.2181749